Topologies
This page is part of MariaDB's Documentation.
The parent of this page is: MariaDB Deployment
Topics on this page:
Overview
MariaDB products can be deployed in many different topologies. The topologies on this page are representative. MariaDB products can be deployed to form other topologies, leverage advanced product capabilities, or combine the capabilities of multiple topologies.
How we describe topologies
Topologies are the arrangement of nodes and links to achieve a purpose. This documentation describes a few of the many topologies that can be deployed using MariaDB database products.
We group topologies by workload (transactional, analytical, hybrid) and technologies (Enterprise Spider). Single-node topologies are listed separately.
To help you select the correct topology:
Each topology is named and this name is used consistently throughout the documentation.
A thumbnail diagram provides a small-scale summary of the topology's architecture.
Finally, we provide a list of the benefits of the topology.
Although multiple topologies are listed on this page, the listed topologies are not the only options. MariaDB products are flexible, configurable, and extensible, so it possible to deploy different topologies that combine the capabilities of multiple topologies listed on this page. The topologies listed on this page are primarily intended to be representative of the most commonly requested use cases.
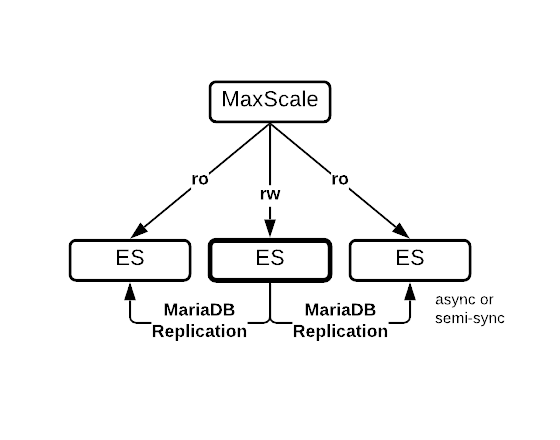
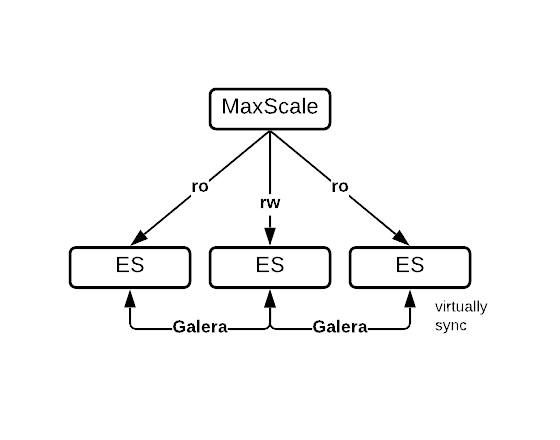
Analytical (OLAP, Data Warehousing, DSS)
Topology | Diagram | Features |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
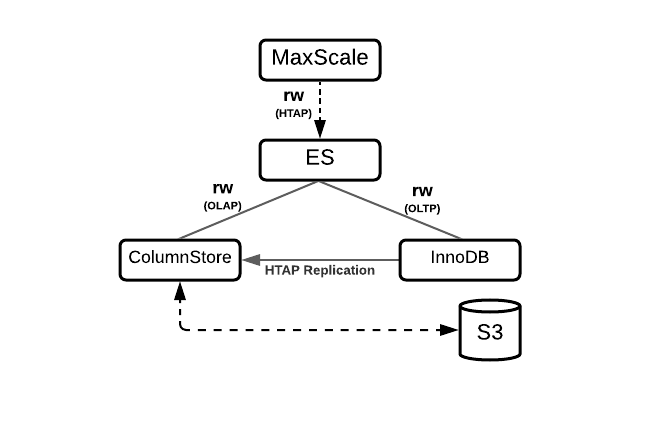
Hybrid Workloads
Topology | Diagram | Features |
|---|---|---|
|
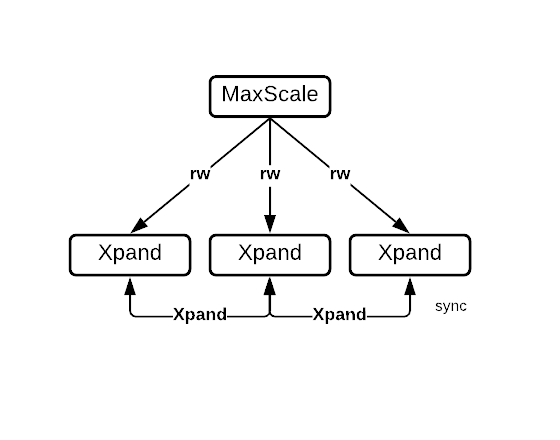
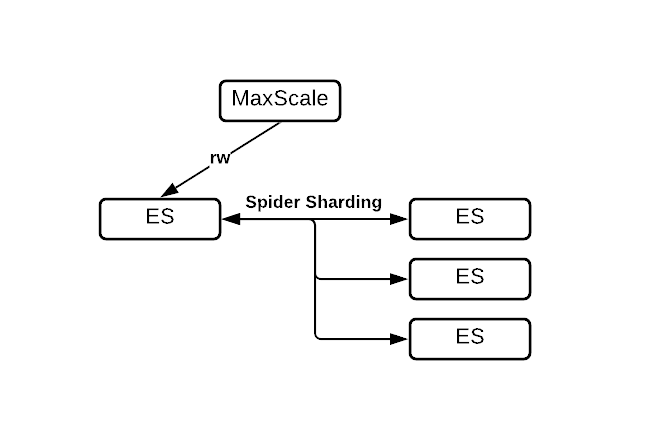
Spider Topologies
Topology | Diagram | Features |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Single Node Topologies
MariaDB Community Server with ColumnStore
MariaDB Enterprise ColumnStore with Local Storage
For high availability and scalability, instead see "ColumnStore Shared Local Storage Topology".
MariaDB Enterprise ColumnStore with Object Storage
For high availability and scalability, instead see "ColumnStore Object Storage Topology".