Deploy Xpand Topology
This page is part of MariaDB's Documentation.
The parent of this page is: Deploy Xpand Topology
Topics on this page:
Overview
This procedure describes the deployment of the Xpand Topology with MariaDB Xpand 5.3 and MariaDB MaxScale 2.5.
MariaDB products can be deployed to form other topologies to leverage advanced product capabilities or combine the capabilities of multiple topologies.
This procedure has 6 steps, which are executed in sequence.
This page provides an overview of the topology, requirements, and deployment procedure.
Please read and understand this procedure before executing.
Procedure Steps
Step | Description |
|---|---|
Step 1 | |
Step 2 | |
Step 3 | |
Step 4 | |
Step 5 | |
Step 6 |
License
A license key is required to use MariaDB Xpand.
MariaDB Xpand license keys can be obtained from MariaDB Sales.
For additional information, see "Licensing for MariaDB Xpand".
Support
Support for this procedure is available in the MariaDB Xpand forum.
Production customers can obtain support in the MariaDB Xpand forum or by submitting a support case.
For additional information, see "Support".
Components
The following components are deployed during this procedure:
Component | Function |
|---|---|
An advanced database proxy, firewall, and query router. | |
Distributed SQL with fault tolerance, write scaling, and horizontal scale-out for transactional workloads. |
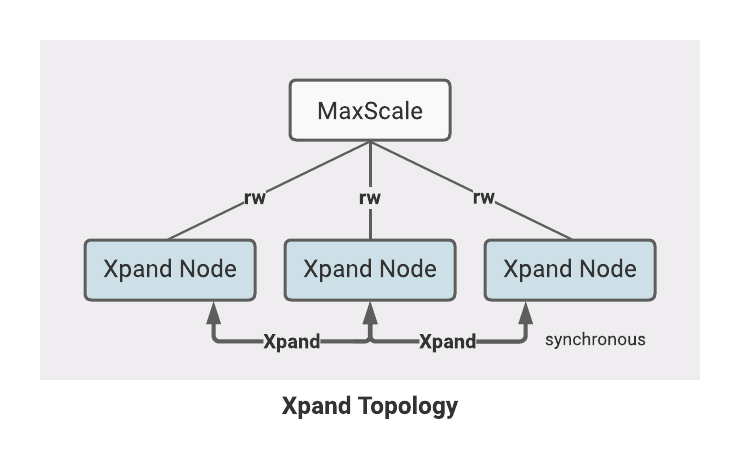
Topology
The Xpand Topology consists of:
One or more MaxScale nodes
Three or more Xpand nodes
The MaxScale nodes:
Monitor the health and availability of each Xpand node using the Xpand Monitor (
xpandmon)Accept client and application connections
Route queries to Xpand nodes using the Read Connection (
readconnroute) or Read/Write Split (readwritesplit) routers.
The Xpand nodes:
Receive queries from MaxScale
Store data in a distributed manner
Execute queries using parallel query evaluation
The Xpand Topology can also be deployed in a multi-zone environment:
Three or more zones
Each zone should be connected by low latency network connections
Each zone must have the same number of Xpand nodes
For additional information, see "MariaDB Xpand Topology".
MariaDB products can be deployed in many different topologies. The topology on this page is representative of basic product capabilities. MariaDB products can be deployed to form other topologies, leverage advanced product capabilities, or combine the capabilities of multiple topologies.
Requirements
These requirements are for the Xpand Topology when deployed with MariaDB Xpand 5.3 and MariaDB MaxScale 2.5.
Minimum System Requirements
Minimum of 3 servers required for a Xpand cluster
Operating System: RHEL or CentOS 7.4+
Between 8 and 32 CPU cores per server
SSDs for database storage
64GB of RAM
Node Count
1 or more MaxScale nodes are required.
3 or more Xpand nodes are required.
To avoid problems establishing quorum during a network partition, it is recommended to deploy an odd number of Xpand nodes. If you deploy nodes in multiple zones, it is recommended to use an odd number of zones.
Production Xpand license keys define the maximum number of Xpand nodes which can be deployed. Up to 128 nodes are supported per Xpand cluster.
Node Sizing
Resource | MaxScale Node | Xpand Nodes |
|---|---|---|
CPU Cores | 8+ | 8-32 |
Memory | 16 GiB | 64 GiB |
Production Xpand license keys define the maximum number of CPU cores which can be deployed.
CPU Recommendations
8-32 physical CPU cores per node
16 or 20 physical cores recommended
Hyper-threading enabled
Memory Recommendations
64GB or more
AWS EC2 Instance Types
MariaDB Xpand 5.3 supports many different instance types in AWS EC2.
All instances in a Xpand cluster must be the same type.
For MariaDB Xpand 5.3, the following EC2 instance types are recommended:
Nitro systems, including but not limited to
c5x,m5x,r5x, andi4i, with SSDs5th generation instances without a
goraafter the56iinstances
For MariaDB Xpand 5.3, the following EC2 instance types are not recommended, so the xpdnode_install.py script throws a warning during installation:
c4d2f1g2g3m3m4p2r4
For MariaDB Xpand 5.3, the following EC2 instance types are rejected, so the xpdnode_install.py script exits with an error during installation:
t2Graviton-based instances
GCP GCE Machine Types
Recommended:
n1-highmem-16n1-standard-16
Not Recommended:
n1-highcpu-16as it has the same CPU power as thehighmemandstandard, yet less RAM
Operating System
In alignment to the enterprise lifecycle, the Xpand Topology with MariaDB Xpand 5.3 and MariaDB MaxScale 2.5 is provided for:
CentOS 7 (x86_
64) Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 (x86_
64)
File System Requirements
Xpand requires the /data/clustrix directory to reside on the ext4 file system or, for Xpand 23.09 and higher, the XFS file system.
For additional information, see "Example File System Configuration for MariaDB Xpand".
Storage Recommendations
Each Xpand node should have 20+ GiB of SSD storage. Mechanical disks and network-attached storage lack sufficient performance to be used for Xpand data (i.e., /data mount point) and are not supported.
Xpand requires database files to be stored on a local SSD-based file system on a separate volume from the root volume containing the OS. This volume should be configured with RAID-0 for best performance and include all of the SSDs to be used for Xpand. For redundancy, Xpand already writes by default two copies of the data so in the event of a node failure or disk failure, the data is still available and don't require higher RAID volume types as that may impact performance. Xpand recommends using the default mount point of /data to simplify installation.
Solid state drives (SSDs) are available in various levels of quality. Xpand recommends using SSDs that have the following characteristics:
Enterprise-class SSDs (not consumer-class available from Amazon.com)
Contains a "Power Loss Protection" feature
Recommend using SSDs manufactured by Intel (every Intel SSD we've seen has Power Loss Protection)
Less performant disks may be used for logs.
The following storage types are recommended:
SATA or NVMe SSDs (for DB data) configured in RAID-0
SATA HDD (for OS, logs, etc)
See the following table for some recommendations:
Purpose | Disk Type | Mount as |
|---|---|---|
Root Volume / OS | Any | / |
Xpand data | SSD only | /data |
Xpand logs | Mechanical OK | /data/xpand/log |
AWS EC2 Storage Recommendations
For best performance, MariaDB recommends Ephemeral SSD storage for database data files
EBS volumes are also supported
GCP GCE Storage Recommendations
SSD Persistent Disk
Size of at least 1 TB per disk to achieve the maximum of 10,000 IOPS per disk
Multiple 1 TB disks may be used for larger storage requirements per VM
Firewall Considerations
Xpand requires a number of ports to be accessible by external applications and for inter-node communication.
One option is to place all Xpand nodes within a secure environment and allow access between all Xpand nodes on all ports.
Another option is to open up the required ports between Xpand nodes.
For additional information, see "TCP Ports for MariaDB Xpand".
DNS Considerations
Xpand requires Xpand node hostnames to be resolvable. Common ways to resolve hostnames are DNS (Domain Name Service) or configuration in /etc/hosts.
Before proceeding with the deployment procedure, ensure that the hostname for each Xpand node is resolvable on all Xpand nodes.
Networking Recommendations
Separate front and back end networks
Back end network should be at least 10 Gbps
10-Gigabit Ethernet switch with enough ports to connect each Xpand server (or 2x switches for redundancy)
AWS EC2 Networking Recommendations
Enhanced Networking must be enabled
Xpand instances must be in a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Xpand instances within an Availability Zone should be in the same Placement Group for best performance
All Xpand instances must be in a Security Group that allows all TCP/UDP traffic within the Security Group (i.e., between Xpand instances)
Xpand clusters deployed across multiple Availability Zones must be within the same region and have <2ms network latency between all nodes
For additional information, see "AWS Security Groups for MariaDB Xpand".
GCP GCE Networking Recommendations
The VPC Network: Firewall rules must be configured to allow all TCP/UDP traffic between all Xpand VMs
Xpand clusters deployed across multiple Zones must be within the same region and have <2ms network latency between all nodes
System User Accounts
By default, Xpand and MaxScale use the following OS user accounts. These accounts are created during the installation process:
User Account | Purpose |
|---|---|
| MaxScale process owner |
| Xpand process owner |
| Used for administrative tasks, such as running the clx command |
For additional information, see "Operating System User Accounts for MariaDB Xpand".
AWS EC2 Load Balancer
Xpand leverages a load balancer to present a single IP to the application servers, and spread DB connections equally across all Xpand instances
Using AWS's Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) is recommended due to its ease of operation
The Network Load Balancer offers the best performance, but requires considerations regarding how the Security Groups are configured
The Classic Load Balancer is easier to configure with Security Groups, but tends to add latency to traffic passing through it
Alternatively, a software load balancer (e.g., HAProxy) running on a separate EC2 instance, or directly on the application server is also suitable
The ELB should be created as an Internal Load Balancer:
GCP GCE Load Balancing
Xpand leverages a load balancer to present a single IP to the application servers, and spread DB connections equally across all Xpand instances
Google Load Balancer:
Select: TCP Load Balancing
Select: Internal facing
Select: Multiple Regions (or not sure yet)
Alternatively, a software load balancer (e.g., HAProxy) running on a separate GCE VM instance, or directly on the application server is also suitable
Quick Reference
MaxScale Configuration Management
MaxScale can be configured using several methods. These methods use the MaxScale REST API.
Method | Benefits |
|---|---|
| |
| |
|
This deployment procedure uses MaxCtrl. Alternatively, MaxGUI or direct REST API access could be used.
MaxScale Service Management
The systemctl command is used to start and stop the MaxScale service.
Operation | Command |
Status |
|
Start |
|
Stop |
|
Restart |
|
Enable startup |
|
Disable startup |
|
View systemd journal |
|
Xpand Service Management
The clx command is used to start and stop the Xpand service.
This command is usually executed as the xpandm system user account. For additional information, see "MariaDB Xpand System User Accounts".
Operation | Command |
|---|---|
Status |
|
Start |
|
Stop |
|
Restart |
|